Seeding a Viable Economic Alternative. Pt 4: Ego-as-Process
his is the fourth and final installment of a series outlining a ‘whole systems’ thinking workshop Arkadian ran with 20 PhD candidates at the Future Connections Conference 2012 in St Andrews, all of whom were conducting PhD Research into Sustainable Development.
In Part 1, we outlined the workshop aims and methodology, and described the main outcome of the session: an Action Plan for seeding a nationwide Viable Alternative to the current economic system.
In Part 2, we discussed 4 Themes that permeated the discussion.
In Part 3, we explored the centrality of the relationship with Nature to the vision of a viable alternative, and also it’s speed of formation and similarities with other workshop outputs.
For the final week, Arkadian would like to talk about another issue they felt is at the heart of the issue: Ego.
And isn’t this just Human Nature? How things are supposed to work? Dawkin’s ‘selfish gene’, Hofstadter’s ‘Social Darwinism’, Rand’s ‘Objectivism’, Smith’s ‘Invisible Hand’, Darwin’s ‘struggle for existence’ etc. etc.? Without leaders, winners and aspirational hierarchies to benchmark our status and successes, apportion our roles, and motivate us to excel, overcome and conquer, wouldn’t we still be scratching out a living among the animals? Ego is the fuel in Civilisation’s engine, an energy that has taken Homo Sapiens further and faster than our forefathers could have ever conceived. Indeed, to the very brink of extinction.
In natural systems – cells, organs, body-minds – a higher hierarchical level only emerges when a lower level problems cannot be solved at their own level. This happens surprisingly rarely. Moreover, Ashby’s Law of Requisite Variety proposes that to be an effective ‘management’ system, and maintain stability, this new level must have equal or a greater information (number of ‘states’) than that which it manages. An everyday analogy might be a manager that only ever appeared at the depot (and got paid) when summoned by the staff to address an intractable issue, and where their capability was evaluated on the basis of a knowledge of the situation which encompassed and surpassed all others present. This happens surprisingly rarely.
So if hierarchy is essentially a solution to problems at the ‘coal face’, how can we have ended up with a world dominated by lofty, teetering, Ivory Towers, of a scale and specialism unparalleled in history? Is this not a textbook example of the tail wagging the dog?
Status is evidently a preoccupation of most animals, particular social ones. It is viewed as a way of ensuring reproductive success and the best genes. Essentially, any behaviour which is more likely to get you a shag or to interrupt your relationship. Status is displayed by a peacock’s tail, lion’s mane, gorilla’s silver back, dancing ability, or dominance abilities and fighting territorial. However preoccupation is short and sweet because there are no levels. Something should be made clear here, is that the obsession with the displays of status is not necessarily synonymous with the obsession with sex.
In primitive tribes (hate that word), e.g. the Golden Bough, how does it work? From my reading, it is either the person best equipped to lead that tribe under the current circumstances, i.e. the one who best embodies variety. If you are a fighting tribe, its a tough guy, if you are a desert tribe, knowledge of the forest and hunting, if you are a Kalahari bushman, the best tracker, and so on. The Golden Bough teaches us that even the ancient kings were of this type, not a lord but a representative of the connection between Man and Nature, liable to quick dispatch if he didn’t fulfill his duties (and sometime chosen as a token May Queen or King, for the purpose of sacrifice).
So what changed? As mentioned in a previous article, there is a strong argument for the theory that ‘management levels’ first appeared in places where there was high population density and an environmental constraint on further growth requiring collective enterprise, most notably during the irrigation projects in Egypt, Mesopotamia, China and India that gave birth to Civilisation. This managerial perspective offered tweaks that enabled a greater productivity, time for reflection which had great benefits for society. However, it also acted like the peacock’s tail, ensuring respect from associates, reproductive success, and survival of the younger. Once people have status, they rarely give it up. Suddenly, for the first time in history we see meritocracy replaced by consolidation of power, in the form of lines of kings, divine right, a priestly class, the caste system. Essentially people of higher status protecting their interests.
Now we have a hierarchy, we are preoccupied by our position in it. What do we do? We have two options. Firstly, we can social clamber we enter a hierarchy, evaluate who are above us and our immediate peers, and then play to the culture of those above, and make it clear that those below are not capable of fulfilling their function without you and that you are superior in your peer group. Secondly, if we’re lucky, our talent is recognised by those above as being able to make them look better, and we rise accordingly. Thirdly, we can create our own, this takes strength and involves setting a identity that is convincing and then gathering followers that reinforce that identity, and therefore your position, and astutely dismissing the rest. The more layers you can create between you and yourself the better. Lastly, we can fastrack it to the top like the ladder that goes from 5 to 99 on the board, possibly the obsession with lotteries and empty celebrity, is a function of the growing gap between rich and poor. How is your success measured: ostensible individiaul wealth!
Thus the bigger the hierarchies get, the more preoccupied we get with our position within them and how we can cheat the rules, to get ahead or by looking ostensibly like we have more when we haven’t. The Spirit Level, demostrates unequivocally the connection between inequality and a range of social ills (see below), that area associated with this preoccupation. And as the rules for climbing favour those who bend the rules, who are best at consolidating their position, over talent, we see increasingly centralisation, and we live in a world which is isolating because we live in a world where its difficult to trust. In short, hierarchies work for those in charge, but not for the world and the people. It is a case of the tail wagging the dog. Worse than this it is Arkadian’s view that hierarchies drive is into an unnatural focus on ourself, isolated by mistrust of others, and a focus on negotiating hierarchies and trusting.
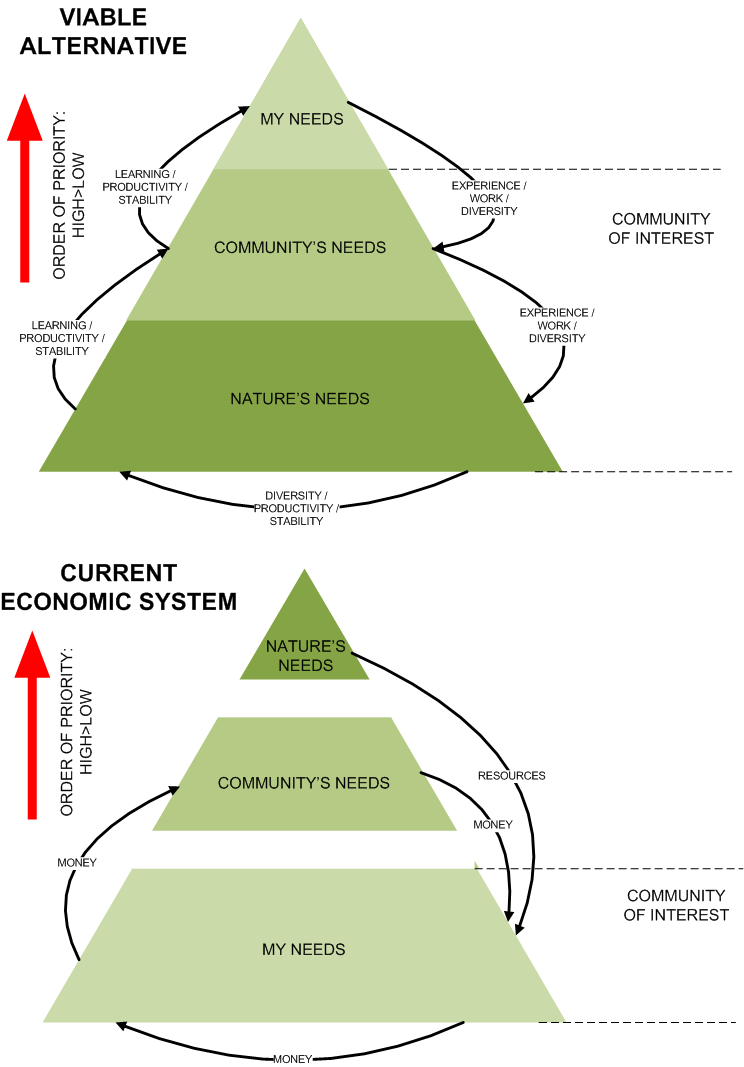
Perhaps, an alternative vision was hinted at in the St Andrew’s outcome. One where cultural purpose is trained by process outwards from the self, and relocated in the enrichment of a natural and social environment, which reciprocates not in fame, a disproportionate share of the goods and begrudging respect, but beauty, stability and freedom for personal expression and growth. Why are we so intent on finding happiness by feeding a black hole, why not try it by feeding the world. Ego is not a thing inside, it is a process, by which we achieve meaning and happiness. The more time we spend working outwards for Nature and others, the more of our brain and memory will be taken up by happiness.
This might be imagined as a reversal of our current motivational hierarchy (see below). The Self may be a natural urge, but maybe, like Disgust, its objects are determined by culture and hierarchies factors.
If so, then possibly the biggest challenge facing the Community-of-Interest is the transition of one state of Self to another, and the management of leadership within such a framework. It is for this reason the group spent so much attention on decision-making processes.
Consonance of collective outcomes. Firstly, it seemed astonishing that a group representing such a miscellany of specialism should take so little time to reach a rough consensus on the structure and soul of a Viable Alternative. It was also interesting that their solution should be unequivocally grass roots, considering that the theses objectives of many present were top-down policy impacts. Intriguingly, their solution also seems remarkably similar in spirit to that envisioned by a diverse group of Occupy Members at a previous Arkadian workshop.
Leave a comment
Recent Posts
- Seeding a Viable Economic Alternative. Pt 3: Placing Mother Nature First
- Seeding a Viable Economic Alternative. Pt 4: Ego-as-Process
- Charlie Hebdo and the Immorality Loop
- My Top 20 Waterfalls Pt3 (S America: #2-1)
- My Top 20 Waterfalls Pt2 (S America: #7-3)
- My Top 20 Waterfalls Pt1 (Africa, Asia, Europe & N America)
- Positive Change using Biological Principles, Pt 4: Principles in Action
- Positive Change using Biological Principles Pt 3: Freedom from the Community Principle
- Positive Change using Biological Principles Pt 2: The missing Community Principle
- Positive Change using Biological Principles, Pt 1: The Campaign Complex
- Seeding a Viable Economic Alternative. Pt 2: The Principal Themes (Outcomes of a Systems Workshop at Future Connections 2012)
- Seeding a Viable Economic Alternative. Pt 1: The Action Plan (Outcomes of a Systems Workshop at Future Connections 2012)
- What I Learned from Destroying the Universe
- Why Corporate Regulation is a Socioenvironmental Necessity. Part 5 of 5: How do We Create a Diverse and Stable Economic System?
- The Root of all Evil: how the UK Banking System is ruining everything and how easily we can fix it.
- What is Occupy? Collective insights from a ‘Whole Systems’ Session with Occupy followers
- Why Corporate Regulation is a Socioenvironmental Necessity. Part 4 of 5: Why does the current Economic System tend towards Uniformity and Instability?
- Why Corporate Regulation is a Socioenvironmental Necessity. Part 3 of 5: Why does A Diverse System = A Stable System?
- Why Corporate Regulation is a Socioenvironmental Necessity. Part 2 of 5: Why does (did) Civilisation tend towards Diversity and Stability?
- Why Corporate Regulation is a Socioenvironmental Necessity. Part 1 of 5: Why do Ecosystems tend towards Diversity and Stability?